
The physical and chemical testing of food is based on the basic theories of physics, chemistry, and physical chemistry of food, as well as national food safety standards. It uses analytical methods to test the composition and content of various types of food, including raw materials, auxiliary materials, semi-finished products, and finished products, to ensure product quality.

Food additives are artificially synthesized or natural substances added to food to improve its quality, as well as its color, aroma, and taste, and for the needs of preservation, freshness, and processing techniques.

Nutritional fortifiers refer to natural or artificially synthesized nutrients and other nutritional components added to food to increase its nutritional value.

Food contaminants are chemical substances that are unintentionally added and pose a hazard to health, which can be introduced during the entire process from production (including crop cultivation, animal breeding, and veterinary drug use), processing, packaging, storage, transportation, sales, consumption, or brought in by environmental pollution.

Mycotoxin refers to secondary toxic metabolites produced by fungi during their growth and reproduction process.

Illegal additives in food refer to substances that are added to food without national permission or without strict inspection, exceeding the requirements and scope of food safety standards, and potentially posing health hazards to humans after consumption.

Pesticide residues refer to any specific substance that appears in food, agricultural products, and animal feed due to the use of pesticides.

Residue of veterinary drugs refers to the presence of all substances related to the drugs in any edible part of food animals after they have been administered medication.
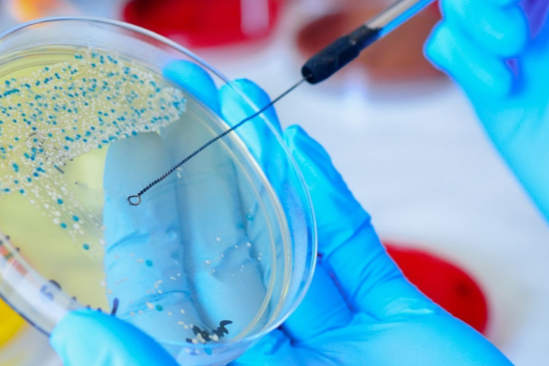
Food microorganisms is the collective term for microorganisms related to food.

Health food efficacy components or signature components are characteristic ingredients that are stable in nature, accurately quantifiable, and have a clear correlation with the health care functions of the product.

To ensure food safety and protect consumer rights, and to prevent counterfeiting and adulteration, food source identification is essential.

